The healthcare industry, long bogged down by administrative burdens and inefficiencies, has found a beacon of hope in the rising tide of automation and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies, once relegated to science fiction, are now poised to revolutionize healthcare delivery, promising to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and empower both healthcare providers and patients. However, the journey from hype to reality is paved with challenges and requires a nuanced understanding of the current landscape and its potential.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been hailed as a revolutionary force in healthcare, with the potential to transform everything from disease diagnosis and treatment to drug discovery and patient care. But amidst the hype, it’s important to ask: where do we stand with AI in healthcare today?
AI in Healthcare (market size worldwide, in bn, from 2021 to 2030)
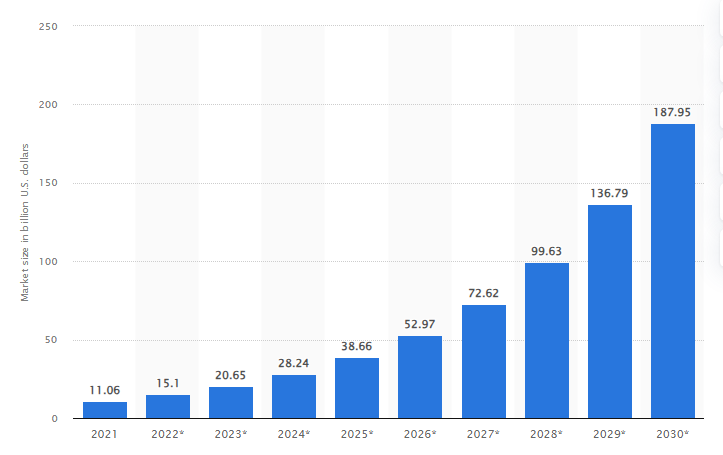
The above graph provides a glimpse into the potential of the AI healthcare market. According to the chart, the market is expected to grow from $20.65bn in 2023 to $28.24bn in 2024 and by 2030 it has the potential to reach $187.95bn worldwide. This rapid growth is driven by a number of factors, including the increasing availability of data, the development of more powerful AI algorithms, large language models and the growing need for more efficient and effective healthcare solutions.
A KPMG survey of healthcare CEOs echoes these findings, with over 75% reporting they have implemented some level of AI technology. Additionally, those CEOs expect the level of investment in AI to grow from 23% of their overall budget today to 35% within the next three year.
· Medical imaging: AI algorithms are being used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to detect diseases with greater accuracy and speed.
· Drug discovery: AI is being used to design new drugs and treatments, as well as to identify potential targets for drug development.
· Personalized medicine: AI is being used to develop personalized treatment plans for patients based on their individual genetic and medical history.
However, despite growing familiarity and initial implementations, most healthcare organizations’ deployments still remain relatively small-scale and narrowly focused. An OPAS (Outpatient Pharmacy Automation System) survey found that while 60% of healthcare delivery organizations are piloting AI tools, only 23% have achieved scale by diffusing the applications across their institutions.
So while healthcare providers acknowledge automation and AI’s potential, this data indicates that many healthcare organizations are still in the early stages of planning and deploying these technologies. However, Covid-19 may serve as a catalyst. McKinsey research shows that the pandemic accelerated the pace of automation and AI adoption across industries by several years. Healthcare was no exception.

The hype around automation and AI in healthcare is centred around several potential major benefits:
· Improved efficiency and cost savings – By automating repetitive administrative tasks, healthcare organizations can reduce costs and allow skilled staff to focus on higher-value work.
· Enhanced patient care – AI tools can help clinicians make faster, more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans for patients. Chatbots and virtual assistants provide patients 24/7 access to health services. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and self-service portals can empower patients to actively manage their health, access information, and schedule appointments, fostering greater involvement in their care journey.
· Better patient outcomes – Analytics tools can aggregate patient data, identify risk factors for diseases, and predict negative outcomes. This allows providers to intervene earlier.
· Precision medicine: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify individual risk factors and predict disease progression, enabling personalized treatment plans and preventive interventions.
· Enhanced clinical decision-making: AI can support clinicians in diagnosis, treatment selection, and medication optimization by providing real-time insights and data-driven recommendations.
· Public health surveillance and disease prevention: AI-powered analytics can track disease outbreaks, identify emerging threats, and inform targeted public health interventions, ultimately saving lives and protecting communities.
Additional advantages include improving clinical decision-making, enabling earlier disease detection, empowering patients with self-service tools, ensuring adherence to treatment plans, and tracking ongoing public health threats.
Some studies have quantified the potential impact of these benefits. Research by Accenture shows that key clinical health AI applications can potentially create $150 billion in annual savings for the US healthcare economy by 2026. Adoption of automation throughout healthcare workflows could save an estimated $165 billion annually.
However, realizing these benefits requires strategic planning around change management, transparent AI, and patient trust. Organizations must provide ample training and leadership to ensure staff understand the intent behind implementing automation technologies.
Other critical success factors include having a clear automation strategy aligned to business goals, choosing the right use cases, ensuring data quality and privacy, monitoring for algorithmic bias, and integrating systems. Leaders also need realistic expectations – implementation can be complex with many cultural barriers. Progress takes thoughtful change management.
As healthcare AI adoption advances from early stages towards maturity over the next decade, institutions, clinicians, and patients alike will both drive and realize its transformative potential. We can expect to see AI support physicians in diagnostic and treatment decisions, help public health organizations predict disease outbreaks, empower patients to monitor and improve their own health, and reinvent operational workflows.
Additionally, the pandemic ushered in a host of new healthcare automation use cases like chatbots for initial patient screening and AI for population health insights. These tools enabled more flexible delivery of health services and data-driven decision-making during an unprecedented public health crisis. Healthcare organizations will continue iterating on and expanding these applications.
In conclusion, despite significant barriers like lack of trust, unproven benefits, and change inertia, automation and AI in healthcare continue marching steadily from hype toward reality. Rather than an overnight disruption, these technologies are steadily integrating into healthcare delivery in focused ways – with the pandemic serving to accelerate a migration already underway. Their promise remains clear – to transform healthcare workflows, improve access and outcomes, and bend the cost curve. While challenges in adoption exist, the digital future rises.
–Amit Kamadollishettaru (Equity Analyst)
For more information on AI and the Medical industry CLICK HERE




